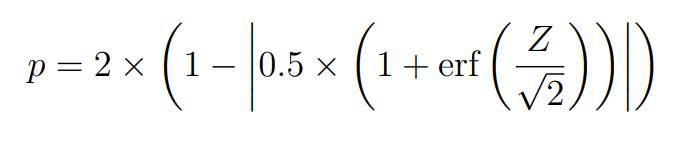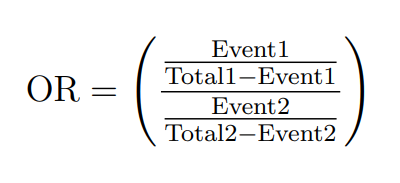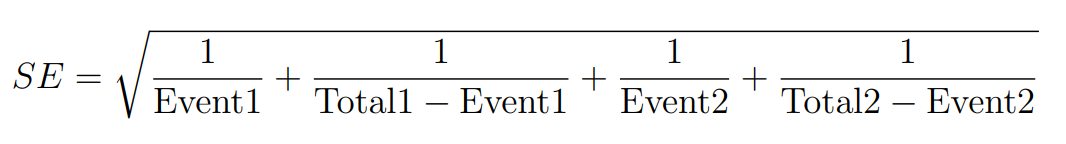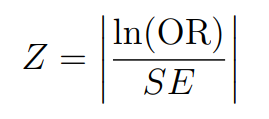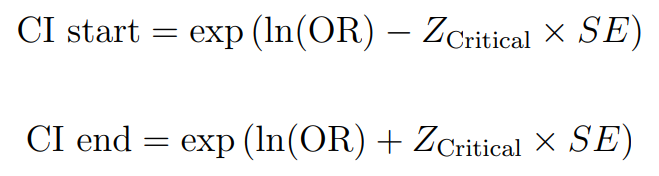Introduction
The odds ratio (OR) is a statistical measure used to quantify the strength and direction of the association between two categorical variables. It is commonly employed in epidemiology, medicine, and other fields where researchers investigate the relationship between exposure to a particular factor and the occurrence of an outcome.
The odds ratio is particularly useful in case-control studies, cohort studies, and clinical trials. It compares the odds of an event happening in one group (e.g., exposed to a risk factor) to the odds of the same event happening in another group (e.g., not exposed to the risk factor). The odds of an event are defined as the probability of the event occurring divided by the probability of it not occurring.
Interpreting the Odds Ratio:
- If the OR is greater than 1, it suggests that the odds of the event are higher in the exposed group compared to the unexposed group.
- If the OR is less than 1, it suggests that the odds of the event are lower in the exposed group compared to the unexposed group.
- If the OR is exactly 1, it indicates no association between the exposure and the outcome.
The odds ratio is a versatile measure that allows researchers to assess the strength of association and make comparisons between groups. It is especially useful when the outcome is binary (e.g., the presence or absence of a disease) and the study involves two groups with different exposures or characteristics.
This article explores the variables involved in the calculator and how the odds ratio, confidence interval, Z-score, and p-value are calculated.
Variables Definitions
- Event 1: The number of occurrences of the event in the first group.
- Total 1: The total number of observations in the first group.
- Event 2: The number of occurrences of the event in the second group.
- Total 2: The total number of observations in the second group.
- Confidence Level: The desired confidence level for the calculation (e.g., 0.90 for 90%, 0.95 for 95%, 0.99 for 99%).
Calculation Formulas
1. Unadjusted Odds Ratio (OR):
2. Standard Error (SE):
3. Z-score:
4. Confidence Interval (CI):
5. P-value: